Screening of Small Molecules Binding to RNA
We are participating in the project "Development of Integrated Database and AI System for RNA-Targeted Drug Discovery Based on Functional Analysis" (FY2021–FY2025) under the AMED program "Drug Discovery Infrastructure Technology Development for Next-Generation Treatment and Diagnosis (RNA-Targeted Drug Discovery Technology Development)." In this project, the Nakatani Group is conducting "screening of small molecules selectively binding to specific sites of RNA" using surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
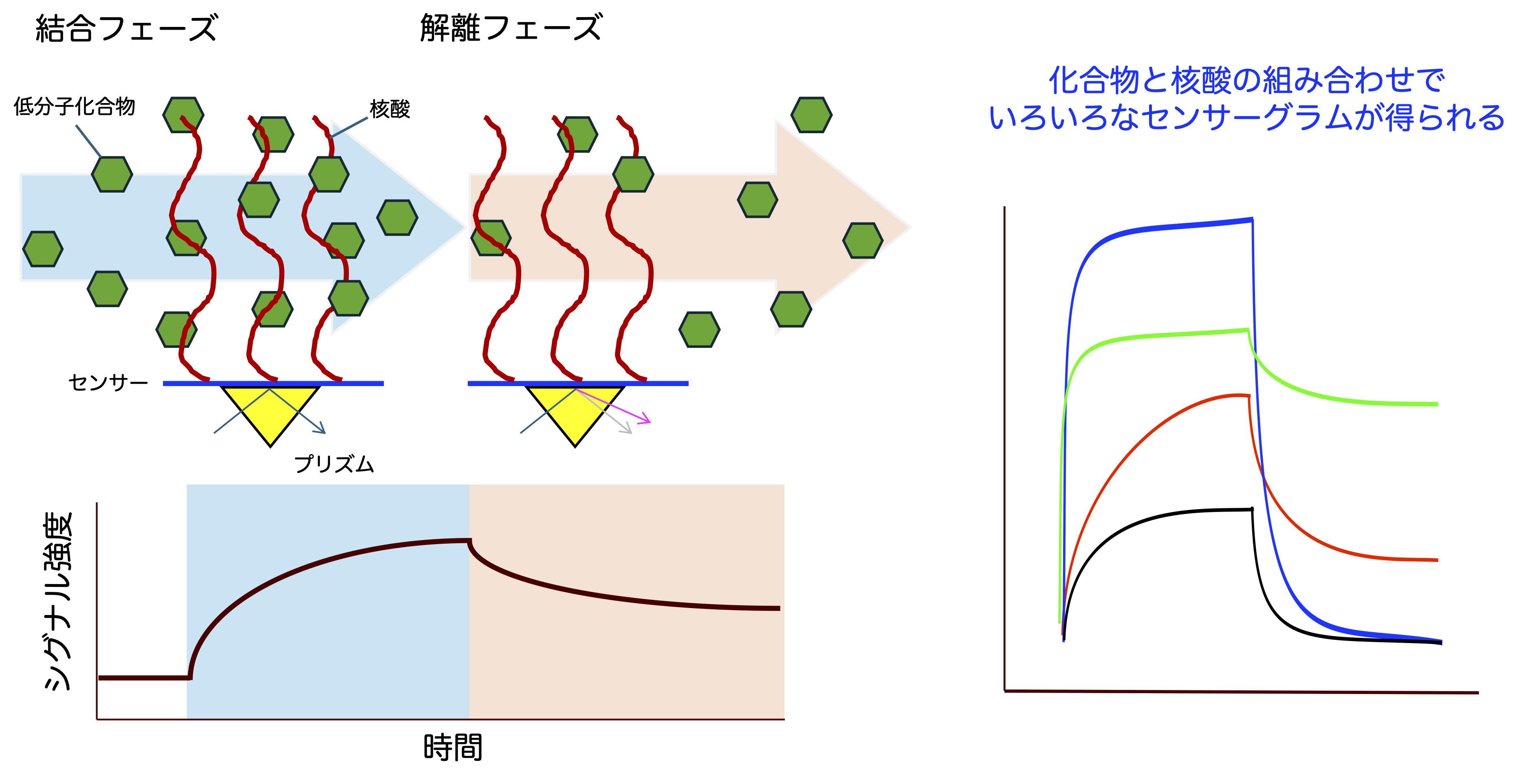
Below is the screening procedure.
SNucleic acids (DNA, RNA) are immobilized on the gold film of the SPR sensor. Compounds are flowed over the sensor together with buffer (binding phase). If a compound binds to the nucleic acid, the SPR signal intensity increases. The bound compound remains on the sensor, and the amount depends on the affinity of the compound for the nucleic acid. After a set time, only buffer is flowed (dissociation phase). The compound gradually dissociates from the nucleic acid and is washed away by the buffer, leading to a decrease in SPR signal intensity. The time course and signal change during the binding and dissociation phases can be treated as characteristic parameters of the compound for the nucleic acid.
We use two SPR instruments: Biacore 8K+ (left) and Biacore T200.

